Article added / Artikel hinzugefügt 01.10.2021
Generally Articles and Discussions about Osteosarcoma in Dogs
→ Evaluations of phylogenetic proximity in a group of 67 dogs with
osteosarcoma: a pilot study
Article added / Artikel hinzugefügt 01.10.2021
Generally Articles and Discussions about Osteosarcoma in Dogs
→ Canine Periosteal Osteosarcoma
Images added / Abbildungen hinzugefügt 02.05.2019
Generally Sonography Atlas of Dogs →
Cardiovascular system → Pulmonary vessels
New subcategory added / Neue Unterkategorie hinzugefügt 02.05.2019
Generally Sonography Atlas of Dogs →
Cardiovascular system → Pulmonary vessels
Images added / Abbildungen hinzugefügt 01.05.2019
Generally Sonography Atlas of Dogs →
Cardiovascular system → Heart valvular diseases



Generally Sonography Atlas of Dogs
(Allgemeiner Sonographie-Atlas von Hunden)
Others
(Sonstiges)
Dog 1. Longitudinal (a) and transversal (b) ultrasound scans of the left submandibular gland - ventral approach. There is enlargement of the gland with a hinomogeneous, hypo echoic parenchyma and small hyperechoic calcific foci (arrows).
D. Lenoci and M. Ricciardi
"Ultrasound and multidetector computed tomography of mandibular salivary gland adenocarcinoma in two dogs"
Open Veterinary Journal, (2015), Vol. 5(2): 173-178

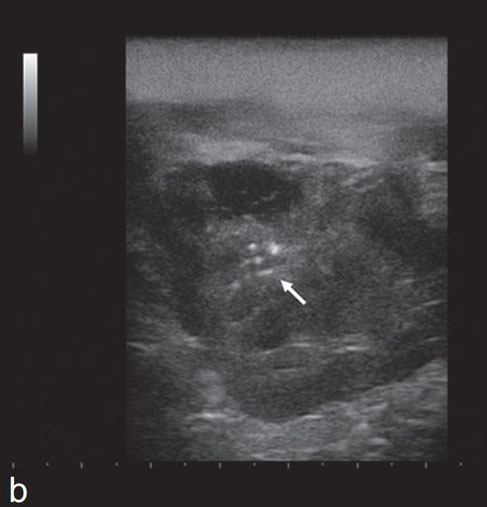
Dog 2. Transverse ultrasound scans of the right submandibular gland, before (a) and after (b) ultrasound guided drainage -ventral approach. The gland is enlarged with anhecoic fluid filled cavity (a, asterisk). The solid component shows heterogeneous echogenicity with small hyperechoic calcific foci (arrows). Residual intraparenchimal fluid (asterisk) and calcific foci (arrow) are seen after drainage of the fluid component (b).
D. Lenoci and M. Ricciardi
"Ultrasound and multidetector computed tomography of mandibular salivary gland adenocarcinoma in two dogs"
Open Veterinary Journal, (2015), Vol. 5(2): 173-178

Dorsal sonographic and diagram (A) of canine anal sac. Dorsal schematic sonograph image (B) of canine anal sac. Anal sac tissue (glands) appears as a hyperechoic thin line (arrow). Asterisks, anal sac contents; e, external sphincter muscle; r, rectum.

Diese Webseite wurde mit Jimdo erstellt! Jetzt kostenlos registrieren auf https://de.jimdo.com