Article added / Artikel hinzugefügt 01.10.2021
Generally Articles and Discussions about Osteosarcoma in Dogs
→ Evaluations of phylogenetic proximity in a group of 67 dogs with
osteosarcoma: a pilot study
Article added / Artikel hinzugefügt 01.10.2021
Generally Articles and Discussions about Osteosarcoma in Dogs
→ Canine Periosteal Osteosarcoma
Images added / Abbildungen hinzugefügt 02.05.2019
Generally Sonography Atlas of Dogs →
Cardiovascular system → Pulmonary vessels
New subcategory added / Neue Unterkategorie hinzugefügt 02.05.2019
Generally Sonography Atlas of Dogs →
Cardiovascular system → Pulmonary vessels
Images added / Abbildungen hinzugefügt 01.05.2019
Generally Sonography Atlas of Dogs →
Cardiovascular system → Heart valvular diseases



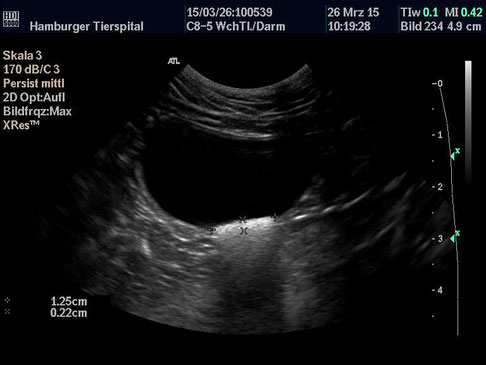
Generally Sonography Atlas of Dogs - Genitourinary system
(Allgemeiner Sonographie-Atlas von Hunden) - (Urogenitales System)
Bladder
(Blase)
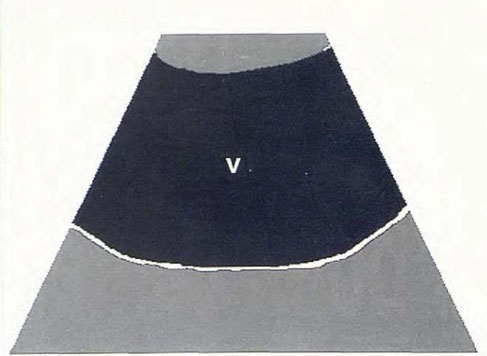
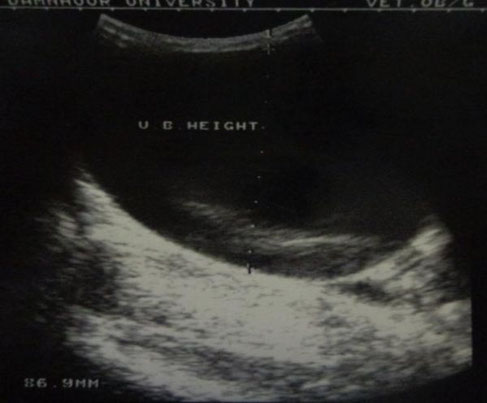
Normal image of the urinary bladder
N. Díez Bru
"Ecografía abdominal en pequeños animales."
CLINICA VETERINARIA DE PEQUEÑOS ANIMALES
Volumen 12, Número 3, Julio/Septiembre 1992

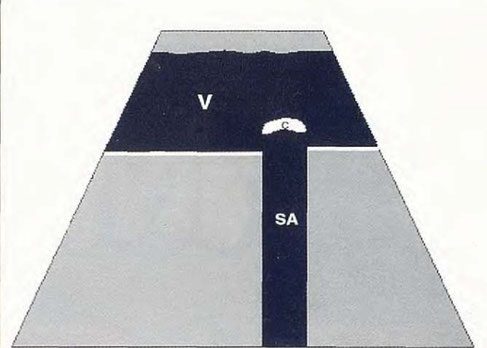
Calculation ( C ) in the bladder that generates an acoustic shadow ( SA ).
N. Díez Bru
"Ecografía abdominal en pequeños animales."
CLINICA VETERINARIA DE PEQUEÑOS ANIMALES
Volumen 12, Número 3, Julio/Septiembre 1992

Blasenstein
(veröffentlicht mit freundlicher Genehmigung der Kleintierpraxis Schaub, Jena, http://www.tierarztpraxis-schaub.de)

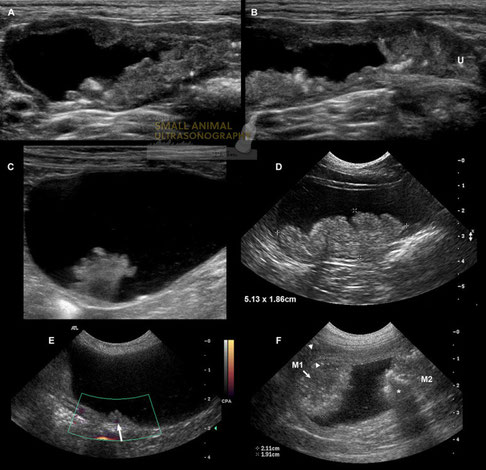
Transitional cell carcinoma (TCC) in dogs.
A: Longitudinal sonogram of an extensive TCC affecting the ventral and dorsal bladder wall, in a 10 year old Lhapsa Apso. B: In the same dog as A. the TCC extends caudally into the bladder neck and urethra (U). C: A cauliflower shaped nodule arising from the craniodorsal wall was found incidentally in a dog presented for urinary obstruction secondary to a urethral calculus. It was confirmed as papillary non infiltrating TCC after surgical removal. D: Longitudinal sonogram of a broad-based hyperechoic mass associated with the craniodorsal bladder wall, consistent with transitional cell carcinoma. E: Longitudinal sonogram in another dog without urinary clinical signs in which focal irregular thickening of the dorsal bladder wall was detected incidentally. Color Doppler signal (arrow) confirmed that this lesion was attached to the bladder wall, as opposed to a blood clot. F: Two separate transitional cell carcinoma masses (M1 and M2) in another dog with mineralization causing acoustic shadowing (*). The arrowheads delineate the apical bladder wall.
With special thanks to the authors of the book "Small Animal Ultrasonography" , Marc-André d’Anjou and Dominique Penninck

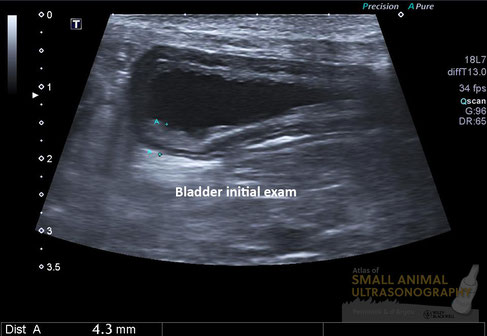
The bladder wall is typically altered in thickness and sometimes in uniformity, shape and contour in cases of cystitis. In this 12 yr-old female Poodle dog presented for chronic dysuria and pollakiuria, this sonographic image was suggestive of cystitis.
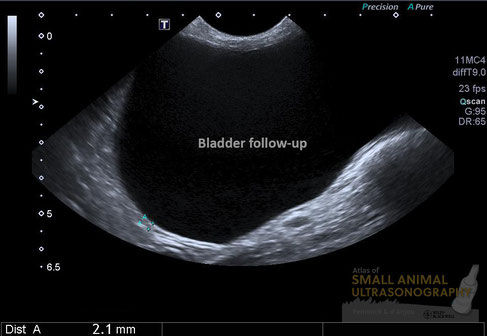
As we know however, the appearance of the bladder wall can be greatly influenced by the amount of luminal distension. And since that dog had been treated with several antibiotics and showed important signs of dysuria, an obstructive lesion remained suspected. It was suggested that a follow-up exam be formed with a full bladder. Here is what was seen on that second exam performed the following day…
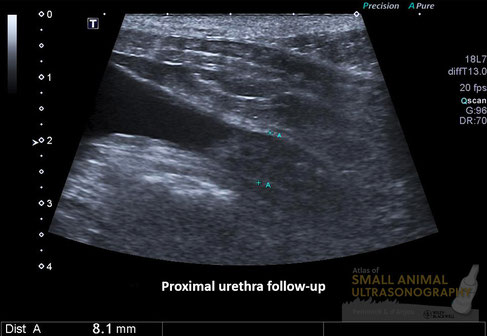
The bladder wall was now smooth and normal in thickness. At the trigone, an irregularity was now detected and urethral wall thickening was now obvious. Ill-defined hyperechoic areas were also noted in the ventral urethral wall suggesting mineralization. These features are consistent with a transitional cell carcinoma, which was masked by the artifactual thickening of the bladder wall due to insufficient distension.
This story is not that remarkable. I’m sure you’ve experienced that more than once. Ultrasound is a great modality. But pitfalls like this one exist – a lot!- and may lead to false diagnoses.
Be careful now not to slip on those ultrasound banana peels! :-)
With special thanks to the authors of the book "Small Animal Ultrasonography" , Marc-André d’Anjou and Dominique Penninck

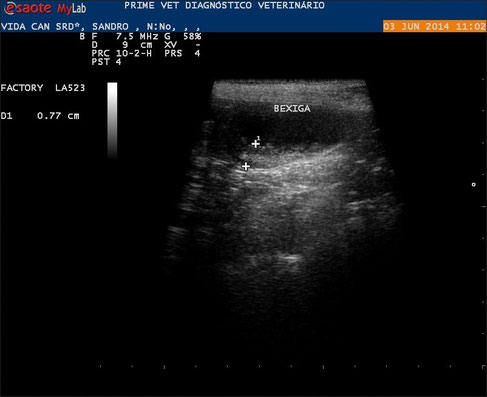
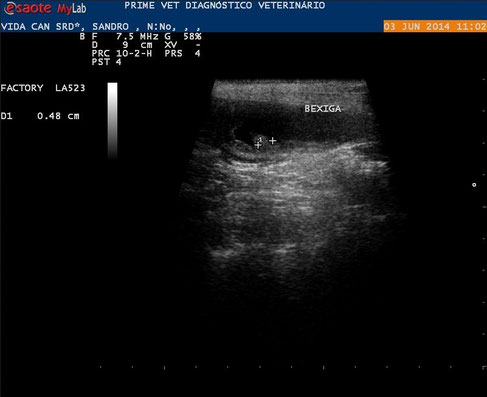
Image of a canine SRD with wall thickening and presence of vegetative form wall.
With special thanks to Priscilla Pinel, Medical Veterinary.
Currently serves in veterinary clinics and homes for the municipality of Rio de Janeiro ( south, north and west ).
http://veterinariapriscillapinel.com.br

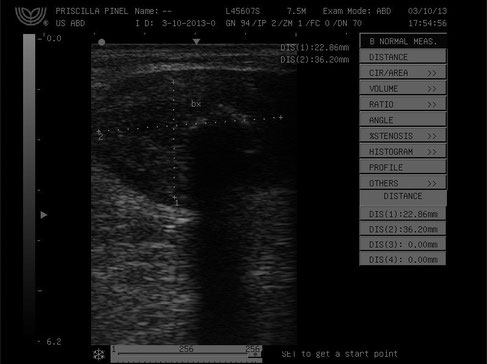
Images of a canine in intraluminal region contact dorsal wall was observed rounded picture defined and irregular margins , heterogeneous , measuring 3.6 cm x 2.2 cm.
With special thanks to Priscilla Pinel, Medical Veterinary.
Currently serves in veterinary clinics and homes for the municipality of Rio de Janeiro ( south, north and west ).
http://veterinariapriscillapinel.com.br

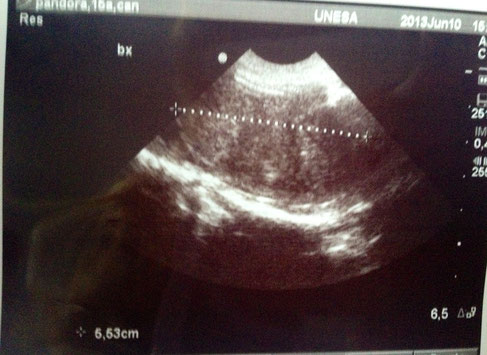
On bladder tumors (or cancer in the urinary bladder ).
Image of a bitch 16 years , with clinical signs of bleeding in the urine.
With special thanks to Priscilla Pinel, Medical Veterinary.
Currently serves in veterinary clinics and homes for the municipality of Rio de Janeiro ( south, north and west ).
http://veterinariapriscillapinel.com.br

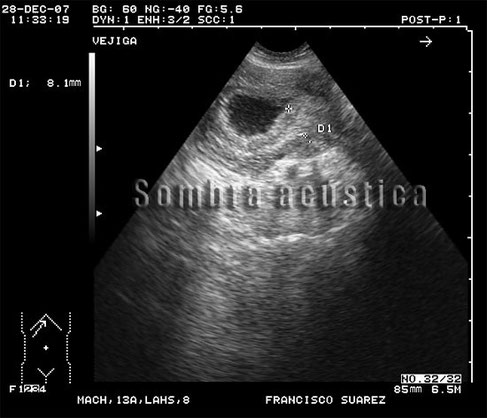
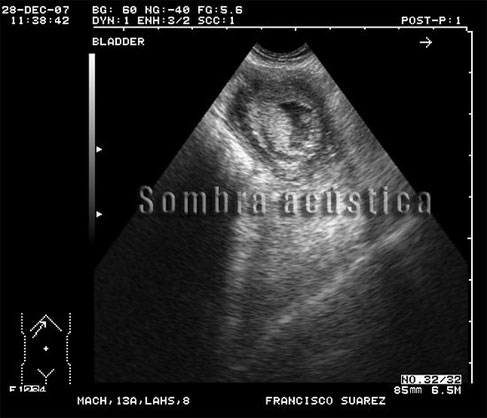
Canine Ultrasound of Bladder Neoplasia.
Patient: Dog breed Lhasa-Apso. Male. 13 years.8kg .
Clinic history: Hematuria and dysuria.
Sonographic findings: Urinary bladder : asymmetric thickening in the bladder outlet.
With special thanks to Irene García Patiño (Sombra Acústica), veterinarian at the Veterinary Clinic Argos in Cee (A Coruña, Spain). http://sombraacustica.com

A sonographic view of a dilated bladder after two days from the onset of acute obstruction. Note the bladder filled with clear anechoic fluid represents urine. An increased dimension over the normal was clear (A). The clear anechoic fluid inside is mixed with some echogenicity representing cystitis. Note the acoustic enhancement in the far field of the image (B).
Gaber E, El-Khamary A, Abdelwahed RE. "Tube Cystostomy VS Bladder Marsupia-lization: Clinical and Ultrasonographic Evaluation in Dogs". www.scopemed.org/?mno=162716 [Access: September 25, 2016]. doi:10.5455/ajvs.162716

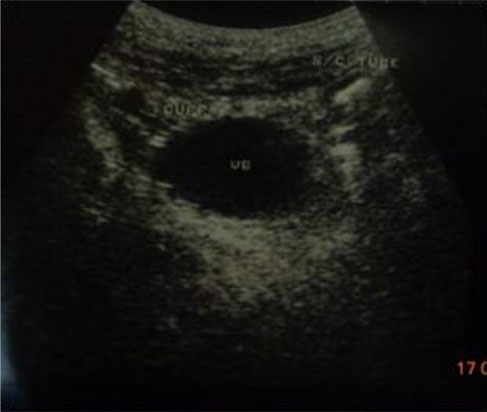
A marsupialized bladder. The stomal canal lateral to the os-penis and originating from lateral bladder wall.
Gaber E, El-Khamary A, Abdelwahed RE. "Tube Cystostomy VS Bladder Marsupia-lization: Clinical and Ultrasonographic Evaluation in Dogs". www.scopemed.org/?mno=162716 [Access: September 25, 2016]. doi:10.5455/ajvs.162716

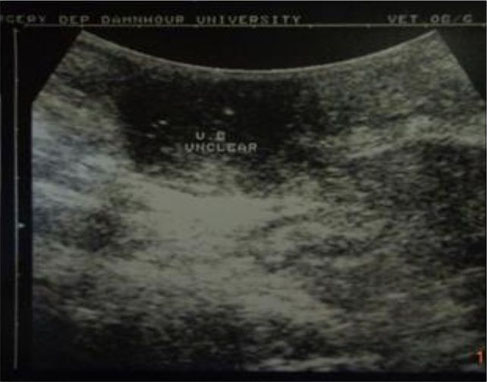
A sonographic view of a marsupialized bladder two days post surgery. Note the unclear bladder content with severe inflammation (cystitis) and fibrosis around the
bladder.
Gaber E, El-Khamary A, Abdelwahed RE. "Tube Cystostomy VS Bladder Marsupia-lization: Clinical and Ultrasonographic Evaluation in Dogs". www.scopemed.org/?mno=162716 [Access: September 25, 2016]. doi:10.5455/ajvs.162716

A marsupialized bladder with narrow occluded stomal canal doesn't open to outside. Note the severe inflammatory reaction and fibrosis found around the bladder and its stomal
canal.
Gaber E, El-Khamary A, Abdelwahed RE. "Tube Cystostomy VS Bladder Marsupia-lization: Clinical and Ultrasonographic Evaluation in Dogs". www.scopemed.org/?mno=162716 [Access: September 25, 2016]. doi:10.5455/ajvs.162716

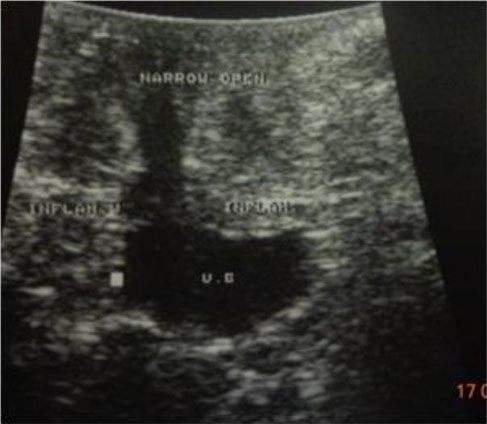
Sonographic image of tube cystostomy bladder three days post surgery. Note the parts of the tube, the cuff and the tube itself running s/c, the bladder still have its normal round to oval shape except of presence of mild inflammatory reaction (cystitis) and around the bladder.
Gaber E, El-Khamary A, Abdelwahed RE. "Tube Cystostomy VS Bladder Marsupia-lization: Clinical and Ultrasonographic Evaluation in Dogs". www.scopemed.org/?mno=162716 [Access: September 25, 2016]. doi:10.5455/ajvs.162716

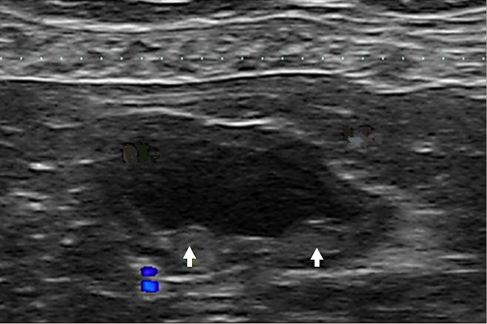
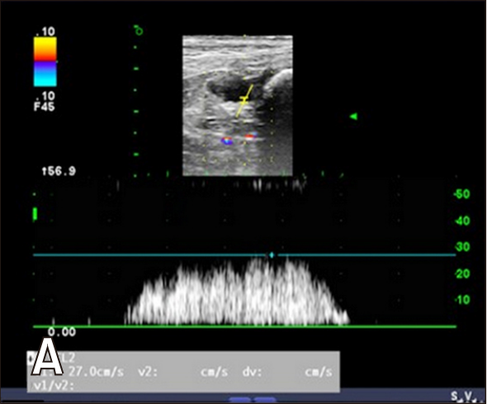
Transverse ultrasonographic image of the urinary bladder showing two small elevations of the mucosal surface
representing the ureteral orifices (arrows) on the dorsal aspect.
Hyunjung Oh , Seongsoo Kim , Suyeon Kim , Jeosoon Lee , Sookyung Yun , Junghee Yoon , Joohyun Jung , Mincheol Choi: "Evaluation of the ureteral jet in dogs by using color Doppler ultrasonography"; J Vet Sci 2017, 18(3), 399-406ᆞhttps://doi.org/10.4142/jvs.2017.18.3.399

Oblique ultrasonographic image of the urinary bladder clearly showing the orifice (A) and the jet flow (B). The anechoic
area within the elevation represents the right ureter (arrows).
Hyunjung Oh , Seongsoo Kim , Suyeon Kim , Jeosoon Lee , Sookyung Yun , Junghee Yoon , Joohyun Jung , Mincheol Choi: "Evaluation of the ureteral jet in dogs by using color Doppler ultrasonography"; J Vet Sci 2017, 18(3), 399-406ᆞhttps://doi.org/10.4142/jvs.2017.18.3.399

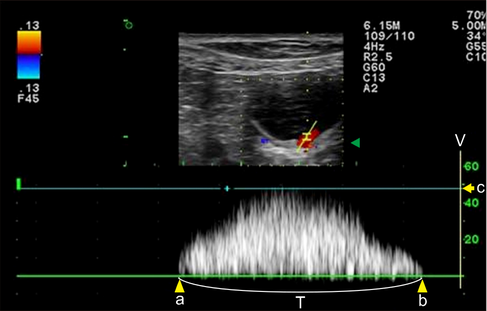
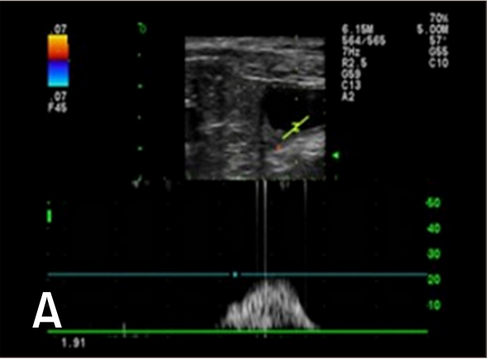
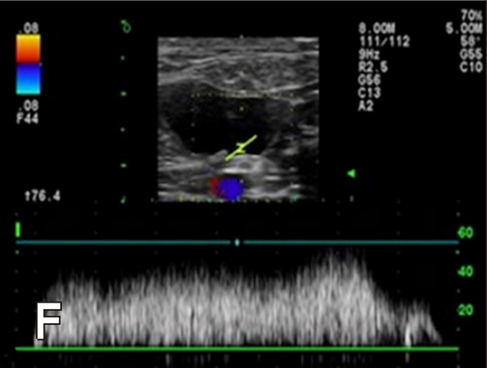
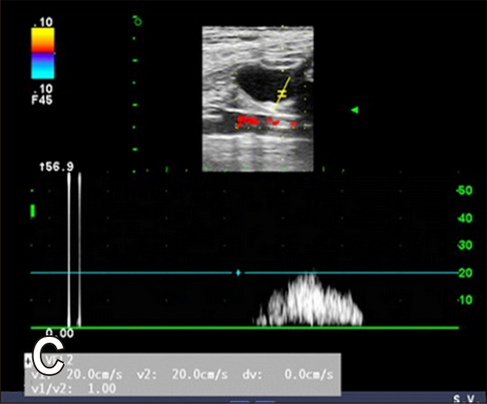
Spectral Doppler image of the right ureteral orifice. The peak velocity (c) is approximately 47.8 cm/sec, and the duration time (T) is 2.0 sec. The waveform is monophasic. a, point of commencement of the Doppler signal; b, termination of signal; V, velocity.
Hyunjung Oh , Seongsoo Kim , Suyeon Kim , Jeosoon Lee , Sookyung Yun , Junghee Yoon , Joohyun Jung , Mincheol Choi: "Evaluation of the ureteral jet in dogs by using color Doppler ultrasonography"; J Vet Sci 2017, 18(3), 399-406ᆞhttps://doi.org/10.4142/jvs.2017.18.3.399

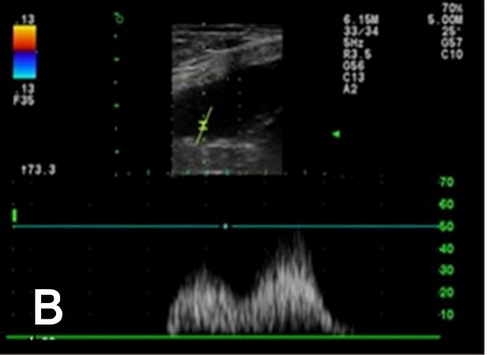
Six distinctive waveform patterns of the ureteral jet. (A) Monophasic waveform. (B) Biphasic waveform. (C) Triphasic waveform. (D) Polyphasic waveform. (E) Square waveform. (F) Continuous waveform.
Hyunjung Oh , Seongsoo Kim , Suyeon Kim , Jeosoon Lee , Sookyung Yun , Junghee Yoon , Joohyun Jung , Mincheol Choi: "Evaluation of the ureteral jet in dogs by using color Doppler ultrasonography"; J Vet Sci 2017, 18(3), 399-406ᆞhttps://doi.org/10.4142/jvs.2017.18.3.399

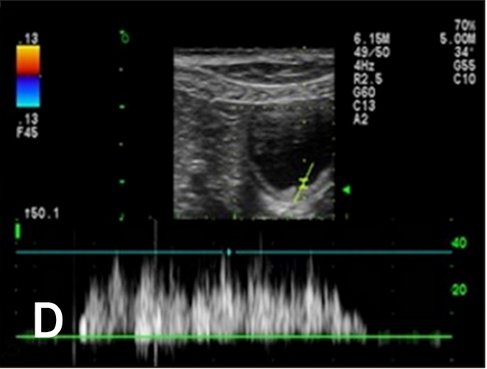
Spectral Doppler images of changing jet appearance and duration.
Hyunjung Oh , Seongsoo Kim , Suyeon Kim , Jeosoon Lee , Sookyung Yun , Junghee Yoon , Joohyun Jung , Mincheol Choi: "Evaluation of the ureteral jet in dogs by using color Doppler ultrasonography"; J Vet Sci 2017, 18(3), 399-406ᆞhttps://doi.org/10.4142/jvs.2017.18.3.399

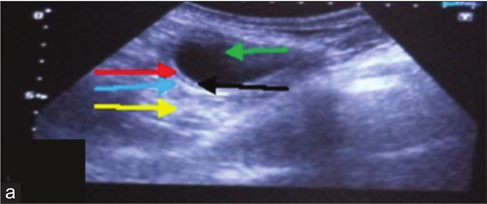
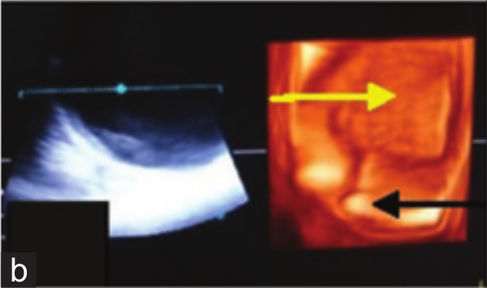
Urinary bladder with cystitis (a) In two-
dimensional the bladder lumen (green arrow), acoustic enhancement (yellow arrow) distally, thickened bladder wall with clear distinction of submucosa (black arrow),
muscularis (red arrow) and serosa (blue arrow). (b) In three-dimensionalthe bladder lumen (black arrow) is visible only without further details.
Dinesh Dehmiwal, S.M.Behl, Prem Singh, Rishi Tayal, Madan Pal and R.K.Chandolia: "Diagnosis of urinary bladder diseases in dogs by using two-dimensional and three-dimensional ultrasonography"; Veterinary World, EISSN: 2231-0916

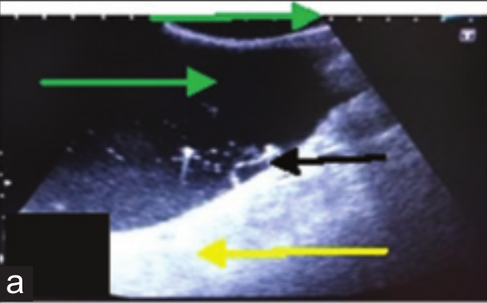
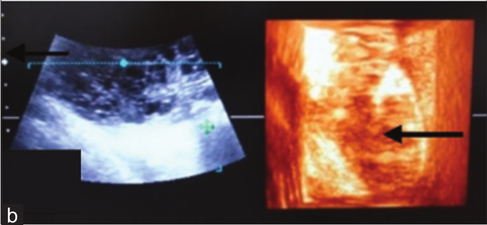
Urinary bladder with cystoliths (a) In two-dimensional the bladder lumen (green arrow), strong acoustic enhancement (yellow arrow) distally, fluctuating pus flakes (black arrow)
and echogenic calculi (red arrow).
(b) In three-dimensional the bladder lumen (yellow arrow) is visible having echogenic calculi (black arrow) in it.
Dinesh Dehmiwal, S.M.Behl, Prem Singh, Rishi Tayal, Madan Pal and R.K.Chandolia: "Diagnosis of urinary bladder diseases in dogs by using two-dimensional and three-dimensional ultrasonography"; Veterinary World, EISSN: 2231-0916

Urinary bladder neoplasia. (a) In two-
dimensional the bladder lumen is obli-terated by a large growth (yellow arrow), focal anechoic areas (red arrow) and small hperechoic dots (green arrow) representing
lumen of blood vessels are also visible in it. (b) In three-dimensional a tissue of mixed echogenicity (black arrow) appears.
Dinesh Dehmiwal, S.M.Behl, Prem Singh, Rishi Tayal, Madan Pal and R.K.Chandolia: "Diagnosis of urinary bladder diseases in dogs by using two-dimensional and three-dimensional ultrasonography"; Veterinary World, EISSN: 2231-0916

Diese Webseite wurde mit Jimdo erstellt! Jetzt kostenlos registrieren auf https://de.jimdo.com