Article added / Artikel hinzugefügt 01.10.2021
Generally Articles and Discussions about Osteosarcoma in Dogs
→ Evaluations of phylogenetic proximity in a group of 67 dogs with
osteosarcoma: a pilot study
Article added / Artikel hinzugefügt 01.10.2021
Generally Articles and Discussions about Osteosarcoma in Dogs
→ Canine Periosteal Osteosarcoma
Images added / Abbildungen hinzugefügt 02.05.2019
Generally Sonography Atlas of Dogs →
Cardiovascular system → Pulmonary vessels
New subcategory added / Neue Unterkategorie hinzugefügt 02.05.2019
Generally Sonography Atlas of Dogs →
Cardiovascular system → Pulmonary vessels
Images added / Abbildungen hinzugefügt 01.05.2019
Generally Sonography Atlas of Dogs →
Cardiovascular system → Heart valvular diseases



Generally Sonography Atlas of Dogs - Genitourinary system
(Allgemeiner Sonographie-Atlas von Hunden) - (Urogenitales System)
Adrenal glands
(Nebennieren)
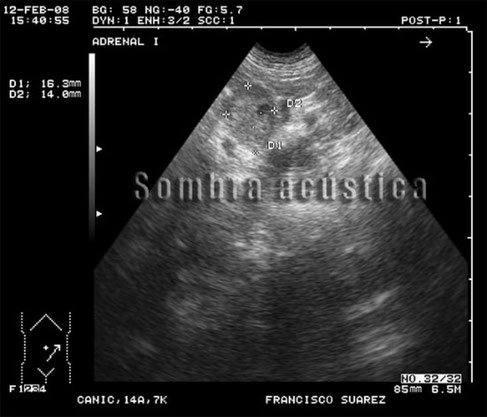
Nebenniere, Hund mit Hyperadrenocorticismus
Mit bestem Dank für die freundliche Genehmigung von Herrn Dr. Giesbert, Tierarztpraxis Franziskus http://www.tierarzt-lünen.de/

Nebenniere, Hund mit Hyperadrenocorticismus, Color-Flow-Doppler-Aufnahme
Mit bestem Dank für die freundliche Genehmigung von Herrn Dr. Giesbert, Tierarztpraxis Franziskus http://www.tierarzt-lünen.de/

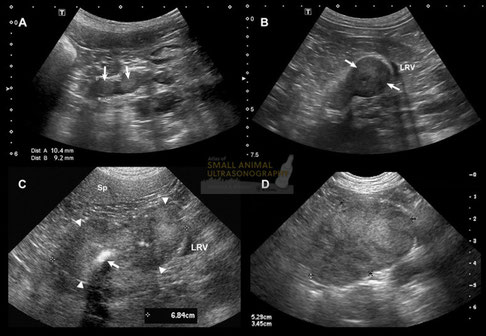
Adrenal nodules and masses in four dogs. A: Sagittal sonogram of the left adrenal gland of a Toy Poodle with pituitary-dependent hyperadrenocorticism. Note the hyperechoic nodules in each pole of the gland, which is thickened (up to 10.4mm). B: Sagittal sonogram of the left adrenal gland of a Mountain Bernese dog with histiocytic sarcoma. A 2cm nodule is identified in the caudal pole of the adrenal gland, deforming the adjacent left renal vein (LRV). Fine-needle aspiration of the nodule confirmed metastasis. C: Transverse sonogram of an adenocarcinoma of the left adrenal gland in an 11-year-old large-breed dog. A large, irregular, inhomogeneous mass (arrowheads) has replaced the left adrenal gland. This mass contains amorphous mineralization, as seen as shadowing hyperechoic foci (arrow),There was no sonographic evidence of vascular invasion, although caudal displacement and compression of the left renal vein (RV) is seen. Sp, spleen. D: Sagittal sonogram of a pheochromocytoma in a 8-year-old boxer crossed. A large inhomogeneous mass is identified medial to the left kidney, but not invading the adjacent vessels.
With special thanks to the authors of the book "Small Animal Ultrasonography" , Marc-André d’Anjou and Dominique Penninck

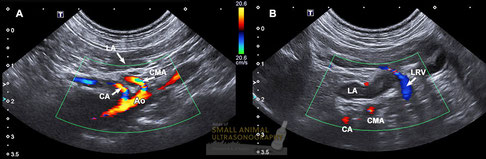
Vascular landmarks for the left adrenal gland in dogs.
A and B: Sagittal sonographic images of a normal left adrenal gland and nearby vascular landmarks in a small breed dog in dorsal recumbency. The left adrenal (LA) lies ventrolateral and somewhat caudal to the celiac artery (CA) and cranial mesenteric artery (CMA), as they exit the aorta (Ao). The gland is also located just cranial to the left renal vein (LRV) that crosses the ventral border of the aorta to reach the caudal vena cava. Note the color pattern of these vessels on color Doppler that depends on the direction of blood flow. Color flow aliasing is recognized as a layered pattern of colors in the central portion of the celiac and cranial mesenteric arteries due to high velocity.
With special thanks to the authors of the book "Small Animal Ultrasonography" , Marc-André d’Anjou and Dominique Penninck

Adrenal adenoma and adenocarcinoma in dogs
With special thanks to the authors of the book "Small Animal Ultrasonography" , Marc-André d’Anjou and Dominique Penninck

Ultrasound guided puncture of canine adrenal gland.
With special thanks to Irene García Patiño (Sombra Acústica), veterinarian at the Veterinary Clinic Argos in Cee (A Coruña, Spain). http://sombraacustica.com

Ultrasound guided puncture of canine adrenal gland.
With special thanks to Irene García Patiño (Sombra Acústica), veterinarian at the Veterinary Clinic Argos in Cee (A Coruña, Spain). http://sombraacustica.com

Enlarged left adrenal gland. Small cyst.
With special thanks to Irene García Patiño (Sombra Acústica), veterinarian at the Veterinary Clinic Argos in Cee (A Coruña, Spain). http://sombraacustica.com

Enlarged left adrenal gland.
With special thanks to Irene García Patiño (Sombra Acústica), veterinarian at the Veterinary Clinic Argos in Cee (A Coruña, Spain). http://sombraacustica.com

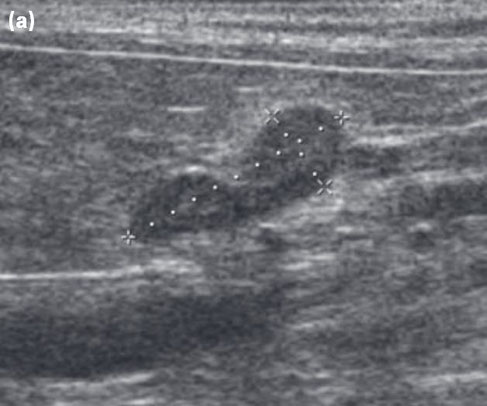
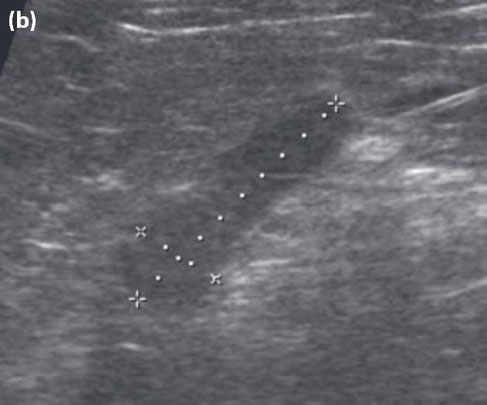
Longitudinal ultrasonography of the adrenal glands recorded in a conscious dog in dorsal recumbency.
(a) Ultrasonography of the left adrenal gland illustrating its typical ‘peanut’ shape in the median plane.
(b) Ultrasonography of the right adrenal gland. For both, adrenal length is represen- ted by the ‘+’ callipers and adrenal width is represented by the ‘x’ callipers.
G Mogicato, Catherine Layssol-Lamour, Fabrice Conchou, Armelle Diquelou, F Raharison, et al.. Ultrasonographic
evaluation of the adrenalglands in healthy dogs: repeatability,reproducibility, observer-dependent variability,and the e
ect of bodyweight, age and sex.
Veterinary Record, BMJ Publishing Group, 2011, 168 (5), pp.130.
<10.1136/vr.c4950>.<hal-01137086>

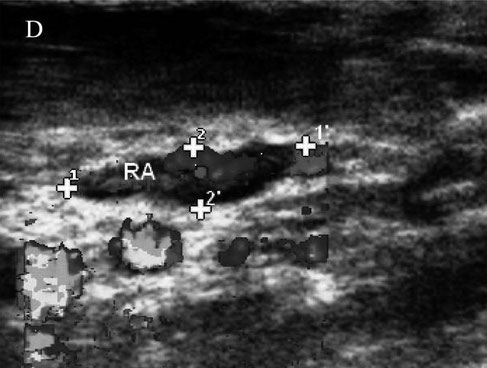
Sagittal view of the right adrenal gland (RA), color-flow Doppler used to differentiate from blood vessels. Cursors represent the length (11’) and the width (22’) of RA.
WICKRAMASEKARA RAJAPAKSHAGE, B. K., ELLEARAEWE GARUHAMILAGE, J. P. K., DE SILVA, D. D. N., & DANGOLLA, A. (2016). "Dimensional ultrasonographic relationship of the right lobe of pancreas with associated anatomic landmarks in clinically normal dogs". http://doi.org/10.1292/jvms.15-0209

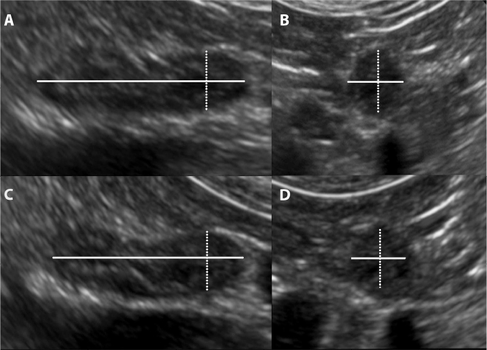
Ultrasound images demonstrating the image plane and location of adrenal gland measurements.
Notes: (A) Dorsal recumbency longitudinal image plane: ultrasound image demonstrating the locations of the length (solid line) and CPT or height (dotted line) measurements. (B) Dorsal recumbency transverse image plane of the caudal pole: ultrasound image demonstrating the locations of the height (dotted line) and width (solid line) measurements. (C) Lateral recumbency longitudinal image plane: ultrasound image demonstrating the location of the length (solid line) and the CPT or width (dotted line) measurements. (D) Lateral recumbency transverse image plane of the caudal pole: ultrasound image demonstrating the location of the width (dotted line) and height (solid line) measurements.
Abbreviation: CPT, caudal pole thickness.
Anne Marie Rose, Thurid Johnstone, Sue Finch, Cathy Beck "The effect of recumbency position on the ultrasound measurement of the canine adrenal gland in non-adrenal gland illness" https://doi.org/10.2147/VMRR.S148725


Ultrasound: Cardiomegaly. Outputs of aorta and cava dilated. Left adrenal gland augmented (15mm in diameter) and with a small cyst.
With special thanks to Irene García Patiño (Sombra Acústica), veterinarian at the Veterinary Clinic Argos in Cee (A Coruña, Spain). http://sombraacustica.com

Ultrasound image of the left and right adrenal glands from a dog with hypoadrenocorticism. Both glands appear flat-tened in contour and largely isoechoic to mildly hypoechoic to the surrounding fat. Subnormal widths (left 0.38 and 0.37 cm, right 0.34 and 0.24 cm) are evident on measurements. Large arrow indicates caudal vena cava and shorter arrow the aorta respectively used as landmarks for the right adrenal gland.
Remo Lobetti (2016) "Retrospective Study of Adrenal Gland Ultrasonography in Dogs with Normal and Ab-normal ACTH Stimulation Test". J Vet Clin Pract petCare 1: 1-6.

Ultrasound image of the left adrenal gland from a normal dog (group 3) demonstrating normal size, rounded contour, and distinct hypoechoic parenchyma compared to surrounding fat.
Remo Lobetti (2016) "Retrospective Study of Adrenal Gland Ultrasonography in Dogs with Normal and Ab-normal ACTH Stimulation Test". J Vet Clin Pract petCare 1: 1-6.

Diese Webseite wurde mit Jimdo erstellt! Jetzt kostenlos registrieren auf https://de.jimdo.com