Article added / Artikel hinzugefügt 01.10.2021
Generally Articles and Discussions about Osteosarcoma in Dogs
→ Evaluations of phylogenetic proximity in a group of 67 dogs with
osteosarcoma: a pilot study
Article added / Artikel hinzugefügt 01.10.2021
Generally Articles and Discussions about Osteosarcoma in Dogs
→ Canine Periosteal Osteosarcoma
Images added / Abbildungen hinzugefügt 02.05.2019
Generally Sonography Atlas of Dogs →
Cardiovascular system → Pulmonary vessels
New subcategory added / Neue Unterkategorie hinzugefügt 02.05.2019
Generally Sonography Atlas of Dogs →
Cardiovascular system → Pulmonary vessels
Images added / Abbildungen hinzugefügt 01.05.2019
Generally Sonography Atlas of Dogs →
Cardiovascular system → Heart valvular diseases



Generally Sonography Atlas of Dogs
(Allgemeiner Sonographie-Atlas von Hunden)
Respiratory system
(Atemwegssystem)
Normal transverse image of the first tracheal ring (A) and the thoracic inlet tracheal ring (B) of a 4-year-old Yorkshire Terrier. An oval shaped hyperechoic tracheal ring (empty arrows) can be seen. The tracheal ring width can be measured between the end points (white arrows) that produce acoustic shadowing. The FTRW and TITRW are 13.4 mm and 11.1 mm, respectively. The sternohyoid (*), sternothyroid (white arrowhead) and sternocephalicus (two arrowheads) muscles are indicated. C: carotid artery, J: jugular vein, Bc: brachiocephalicus muscle, Lc: longus capitis muscle, TG: thyroid gland.
Authors: Kidong Eom1, Kumjung Moon2, Yunsang Seong2, Taeho Oh3, Sungjoon Yi4, Keunwoo Lee3, Kwangho Jang2
Publication date ( Electronic ): 31 December 2008
Source: PMC ID: 2811782
Journal: Journal of Veterinary Science
Publisher: The Korean Society of Veterinary Science

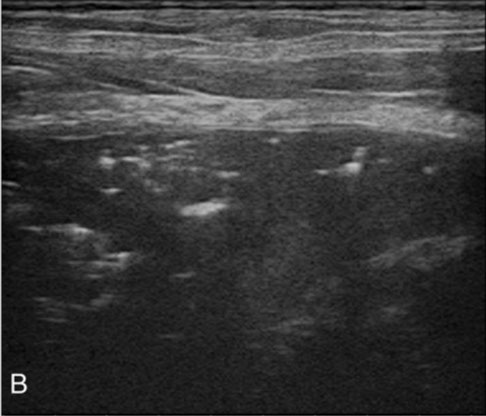
Transverse image in a 7-year-old Miniature Poodle with severe tracheal collapse. The first tracheal ring (A) shows a semicircular shadow, but the thoracic inlet tracheal ring (B) is flattened and displaced laterally. The sternohyoid muscle (*) and carotid artery (C) are seen. The FTRW (white arrows) and TITRW (black arrows) are 11.3 mm and 17.1 mm, respectively.
Authors: Kidong Eom1, Kumjung Moon2, Yunsang Seong2, Taeho Oh3, Sungjoon Yi4, Keunwoo Lee3, Kwangho Jang2
Publication date ( Electronic ): 31 December 2008
Source: PMC ID: 2811782
Journal: Journal of Veterinary Science
Publisher: The Korean Society of Veterinary Science

Pulmonary sonography. Scattered small sub pleural solid nodules.
Angela Di Cesare, Donato Traversa, Simone Manzocchi, Silvana Meloni, Eleonora Grillotti, Edoardo Auriemma, Fabrizio Pampurini, Cecilia Garofani, Fabrizio Ibba and Luigi Venco
"Elusive Angiostrongylus vasorum infections",
DOI 10.1186/s13071-015-1047-3

Pulmonary sonography. Largest small sub pleural solid nodule, diameter ~5
mm.
Angela Di Cesare, Donato Traversa, Simone Manzocchi, Silvana Meloni, Eleonora Grillotti, Edoardo Auriemma, Fabrizio Pampurini, Cecilia Garofani, Fabrizio Ibba and Luigi Venco
"Elusive Angiostrongylus vasorum infections",
DOI 10.1186/s13071-015-1047-3

Post-treatment pulmonary sonography. No sub-pleural nodules can be visualized.
Angela Di Cesare, Donato Traversa, Simone Manzocchi, Silvana Meloni, Eleonora Grillotti, Edoardo Auriemma, Fabrizio Pampurini, Cecilia Garofani, Fabrizio Ibba and Luigi Venco
"Elusive Angiostrongylus vasorum infections",
DOI 10.1186/s13071-015-1047-3

Echocardiography. Right parasternal short axis view, slightly oblique for pulmonary trunk and right pulmonary artery optimal visualization. The pulmonary arteries do not appear
dilated but filarid echoes are present (white square) within the right pulmonary artery
Angela Di Cesare, Donato Traversa, Simone Manzocchi, Silvana Meloni, Eleonora Grillotti, Edoardo Auriemma, Fabrizio Pampurini, Cecilia Garofani, Fabrizio Ibba and Luigi Venco
"Elusive Angiostrongylus vasorum infections",
DOI 10.1186/s13071-015-1047-3

Lung sonography. Small scattered well defined focallesions into the subpleural pulmonary parenchyma
Angela Di Cesare, Donato Traversa, Simone Manzocchi, Silvana Meloni, Eleonora Grillotti, Edoardo Auriemma, Fabrizio Pampurini, Cecilia Garofani, Fabrizio Ibba and Luigi Venco
"Elusive Angiostrongylus vasorum infections",
DOI 10.1186/s13071-015-1047-3

Lung sonography. Lung consolidation (hepatization) of left caudal lung lobe
Angela Di Cesare, Donato Traversa, Simone Manzocchi, Silvana Meloni, Eleonora Grillotti, Edoardo Auriemma, Fabrizio Pampurini, Cecilia Garofani, Fabrizio Ibba and Luigi Venco
"Elusive Angiostrongylus vasorum infections",
DOI 10.1186/s13071-015-1047-3

Ultrasonographic study (transverse plane) performed at the level of the fifth intercostal space of the right ventral thoracic wall. The right middle lobe (RmL) has sharp margins,
is small in size, atelectatic and retracted medially. The right caudal lobe (RCdL) is partially aerated. Lateral to both of these lobes, along the thoracic wall, there is a mass in the right
caudal hemithorax, with rounded margins, characterised by a liver-like echogenic tip and multiple gas bubbles reverberating in its central portion (arrow heads). This finding confirmed the
corresponding vesicular gas pattern observed in the radiographs. This mass is the right cranial lung lobe (RCrL) (long arrow). An anechoic unilateral mild pleural effusion (PE) surrounds the lung
lobes. (L: lateral; M: medial; Cd: caudal; Cr cranial.).
E Terzo, J Pink, A Puggioni, R Shiel, V Andreoni and H McAllister, "Right cranial lung lobe torsion after a diaphragmatic rupture repair in a Jack Russell terrier"
doi:10.1186/2046-0481-61-3-170
http://www.irishvetjournal.org/content/61/3/170

Gesunde Lunge eines 4-jährigen Dachshundes, man sieht sehr deutlich das Zwerchfell und die anschliessende Lungenstruktur

Pulmonary metastases in two dogs. A. A small, round, soft tissue opacity is noted on this left lateral thoracic radiograph (arrow) of a Dalmatian with a history of weight loss. B. Using a left intercostal approach, a spherical hypoechoic nodule is seen at the superficial aspect of the lung (L). Ultrasound guided fine-needle aspirate revealed a metastatic sarcoma. An abdominal fibrosarcoma was also detected. C. This lateral thoracic radiograph in an 8-year-old Golden Retriever with a 2 week history of cough, showed numerous small soft tissue nodules affecting all lung lobes. D. Using both left and right intercostal approaches, numerous small, hypoechoic nodules (arrowheads) were observed at the superficial aspect of the lung. Fine-needle aspiration by using ultrasound guidance revealed a histiocytic sarcoma.
With special thanks to the authors of the book "Small Animal Ultrasonography" , Marc-André d’Anjou and Dominique Penninck

Ultrasound examination of a male 3-year-old Boxer. The B-mode ultrasound examination shows the phreno-pericardial ligament (white arrows), confirming the presence of a large quantity of free fluid (FF) in the pleural space (Figure D) and the presence of an atelectatic lung lobe (arrows).
Pires, Sâmara Turbay, Hage, Maria Cristina Ferrarini Nunes Soares, Pinto, Ana Carolina Brandão de Campos Fonseca, & Hagen, Stefano Carlo Filippo. (2015). "Comparative study between radiology and ultrasound in the evaluation of extracardiac thoracic diseases in dogs and cats". https://dx.doi.org/10.1590/0103-8478cr20140192

Ultrasound examination of a 15-year-old female Cocker. The B-mode ultrasound examination (Figure D), viewed from the entrance of the thorax, demonstrates a mass with heterogeneous echogenicity and echotexture. The mass has irregular borders and is in the area of the sternal lymph nodes, demonstrates calcifications dispersed throughout the tissue and forms an acoustic shadow (white arrows). The same mass is visualized at the lateral edge of the thorax (Figure E). Power Doppler evaluation shows a mottled central vascularization pattern (Figure F).
Pires, Sâmara Turbay, Hage, Maria Cristina Ferrarini Nunes Soares, Pinto, Ana Carolina Brandão de Campos Fonseca, & Hagen, Stefano Carlo Filippo. (2015). "Comparative study between radiology and ultrasound in the evaluation of extracardiac thoracic diseases in dogs and cats". https://dx.doi.org/10.1590/0103-8478cr20140192

Ultrasound examination of a 17-year-old male mixed breed dog. B-mode ultrasound examination (Figures D and E) shows a small quantity of free fluid (FF) in the pleural space in the right hemithorax. Note the echoic right lung lobe (consolidation) with the presence of fluid bronchograms (black arrows). The Doppler ultrasound examination (Figure F) confirms that the structure with hyperechoic borders is a fluid bronchogram rather than a vessel.
Pires, Sâmara Turbay, Hage, Maria Cristina Ferrarini Nunes Soares, Pinto, Ana Carolina Brandão de Campos Fonseca, & Hagen, Stefano Carlo Filippo. (2015). "Comparative study between radiology and ultrasound in the evaluation of extracardiac thoracic diseases in dogs and cats". https://dx.doi.org/10.1590/0103-8478cr20140192

Ultrasound image of normal thoracic wall; hyperechoic line (arrows) corresponds to pleural line.
Simonetta C, Valentina D, Tommaso M (2017) Thoracic Ultrasound: A Method for the Work-Up in Dogs and Cats with Acute Dyspnea. J Anim Sci Res 1(1): dx.doi.org/10.16966/2576-6457.104

Thoracic wall; starting from the pleural line some hyperechoiclines (B-lines), due to ring down artefacts, are evident; pleura is regular and not thickened in a patient with cardiogenic pulmonary edema
Simonetta C, Valentina D, Tommaso M (2017) Thoracic Ultrasound: A Method for the Work-Up in Dogs and Cats with Acute Dyspnea. J Anim Sci Res 1(1): dx.doi.org/10.16966/2576-6457.104

Shred sign image in a patient with pneumonia. It is possible to notice the peripheral pulmonary consolidation with irregular reverberation areas and central air bronchogram.
Simonetta C, Valentina D, Tommaso M (2017) Thoracic Ultrasound: A Method for the Work-Up in Dogs and Cats with Acute Dyspnea. J Anim Sci Res 1(1): dx.doi.org/10.16966/2576-6457.104

US detection of B-lines associated with irregular, thickened pleural line and sub-pleural consolidations in a patient with ARDS
Simonetta C, Valentina D, Tommaso M (2017) Thoracic Ultrasound: A Method for the Work-Up in Dogs and Cats with Acute Dyspnea. J Anim Sci Res 1(1): dx.doi.org/10.16966/2576-6457.104

Anticoagulants intoxication in a dog; (left) day one, note the presence of confluents B-lines that provides white lung aspect. (right) day two, modification of the image with pulmonary consolidation and air bronchogram.
Simonetta C, Valentina D, Tommaso M (2017) Thoracic Ultrasound: A Method for the Work-Up in Dogs and Cats with Acute Dyspnea. J Anim Sci Res 1(1): dx.doi.org/10.16966/2576-6457.104

Lung ultrasound images. (A) Absent B‐lines (no B‐lines). (B) Rare B‐lines (≤3 B‐lines). (C) Numerous B‐lines (>3 B‐lines). (D) Confluent B‐lines (multiple B‐lines blended together).
Vezzosi T, Mannucci T, Pistoresi A, et al. Assessment of Lung Ultrasound B-Lines in Dogs with Different Stages of Chronic Valvular Heart Disease. J Vet Intern Med. 2017;31(3):700–704. doi:10.1111/jvim.14692

Ultrasonographic evaluation of disseminated neoplastic lesions on the pleura. Small nodules of 1-1.3 mm size on the surface of the pleura, exhibiting homogeneous low echogenicity inside with a hypoechoic structure, were identified, which had not been noted at the early stage of the disease, via detailed ultrasonographic examination using a high frequency linear probe (A, arrows). The adjacent normal pleurae were delineated as finely hyperechoic linear structures (B, arrow-heads). The nodules gradually increased in size and number on the parietal pleura (C, arrows) as well as the visceral pleura and diaphragm (D, arrows). Arrowheads, parietal pleura; TW, thoracic wall; PE, pleural effusion; DP, diaphragm; PL, lung; LIV, liver. Scale bar = 0.5 cm.
Nabeta Rina, Nakagawa Yuki, Chiba Shiori, Xiantao Hou, Usui Tatsuya, Suzuki Kazuhiko, Furuya Tetsuya, Fukushima Ryuji, Uchide Tsuyoshi: "Pericardial Mesothelioma in a Dog: The Feasibility of Ultrasonography in Monitoring Tumor Progression"; Front. Vet. Sci., 18 April 2019 | https://doi.org/10.3389/fvets.2019.00121

Diese Webseite wurde mit Jimdo erstellt! Jetzt kostenlos registrieren auf https://de.jimdo.com