Article added / Artikel hinzugefügt 01.10.2021
Generally Articles and Discussions about Osteosarcoma in Dogs
→ Evaluations of phylogenetic proximity in a group of 67 dogs with
osteosarcoma: a pilot study
Article added / Artikel hinzugefügt 01.10.2021
Generally Articles and Discussions about Osteosarcoma in Dogs
→ Canine Periosteal Osteosarcoma
Images added / Abbildungen hinzugefügt 02.05.2019
Generally Sonography Atlas of Dogs →
Cardiovascular system → Pulmonary vessels
New subcategory added / Neue Unterkategorie hinzugefügt 02.05.2019
Generally Sonography Atlas of Dogs →
Cardiovascular system → Pulmonary vessels
Images added / Abbildungen hinzugefügt 01.05.2019
Generally Sonography Atlas of Dogs →
Cardiovascular system → Heart valvular diseases



Generally Sonography Atlas of Dogs
(Allgemeiner Sonographie-Atlas von Hunden)
Nervous system
(Nervensystem)
Transverse ultrasonographic scans of the carpal canal at the proximal (P) and the distal (D) levels of the carpal canal. Color Doppler imaging is helpful to easily localize the median nerve. Note that the size of the median nerve is larger at the proximal part of the carpal canal as compared to the distal part. The transverse diameter (A) and the posteroanterior diameter (B) of the median nerve, the median nerve (MN), the median artery (MA), the deep digital flexor (DDFT) tendons and the superficial digital flexor tendons (SDFT).
Authors: Erkut Turan1, Yelda Ozsunar2, Ismail Gokce Yildirim1
Publication date ( Electronic ): 31 March 2009
Source: PMC ID: 2801093
Journal: Journal of Veterinary Science
Publisher: The Korean Society of Veterinary Science

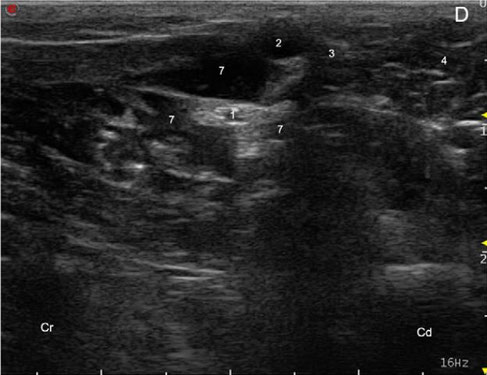
Sciatic(ScN) and femoral (FN) nerve
(C) Corresponding transverse ultrasound image of the ScN. The two components of the ScN are readily distinguished and appear as two hypoechoic tubular st
ructures surrounded by a thin hyperechoic rim. (1*) peroneus communis nerve, and (1**) tibialis nerve. (D) Local anaesthetic solution surrounding the ScN showing the characteristic ‘donut sign’.
(1) ScN, (2) biceps femoris muscle, (3) femur, (4) adductor magnus muscle, (5) local anaesthetic solution. Prox, proximal; Dis, distal; Cr, cranial; Cd, caudal; Med, medial; Lat,
lateral.
Diego F. Echeverry, Francisco Gil, Francisco Laredo, Maria Dolores Ayala, Eliseo Belda, Marta Soler, Amalia Agut
"Ultrasound-guided block of the sciatic and femoral nerves in dogs: A descriptive study"

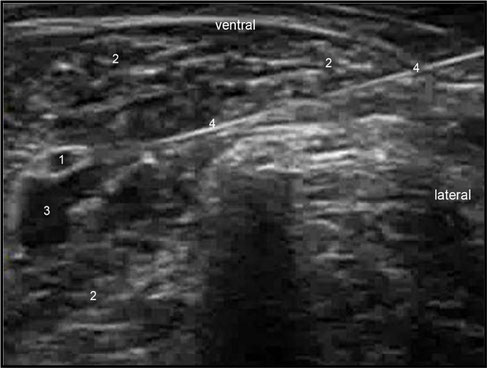
Sciatic(ScN) and femoral (FN) nerve
(C) Corresponding transverse US image of femoral nerve. (D) Local anaesthetic solution surrounding the FN. (1) FN, (2) femoral artery, (3) femoral vein, (4) pectineus muscle, (5) femur, (6)
iliacus fascia, (7) local anaesthetic solution. Prox, proximal; Dis, distal; Cr, cranial, Cd, caudal; Med, medial; Lat, lateral.
Diego F. Echeverry, Francisco Gil, Francisco Laredo, Maria Dolores Ayala, Eliseo Belda, Marta Soler, Amalia Agut
"Ultrasound-guided block of the sciatic and femoral nerves in dogs: A descriptive study"

(C) Corresponding transverse ultrasound image of the FN and related structures. (D) Ultrasonographic image showing the approach of the needle towards the FN. (E) Local anaesthetic (LA) agent
surrounding the FN showing the characteristic ‘donut sign’.
(1) FN, (2) iliopsoas muscle, (3) ileum, (4) vertebral body, (5) quadratus lumborum muscle, (6) abdominal wall, (7) urinary bladder, (8) descending colon, (9) common iliac vein, (10) external
iliac artery, (11) needle, (12) LA. Cr, cranial; Cd, caudal; Med, medial; Lat, lateral; Vent, ventral; Dor, dorsal.
Diego F. Echeverry, Francisco G. Laredo, Francisco Gil, Eliseo Belda, Marta Soler, Amalia Agut
"Ventral ultrasound-guided suprainguinal approach to block the femoral nerve
in the dog"
doi: 10.1016/j.tvjl.2011.06.043

Transverse ultrasonographic image obtained by a ventral SIA: (1) FN, (2) Iliopsoas muscle, (3) spread of injectate, (4) needle.
Diego F Echeverry, Francisco G Laredo, Francisco Gil, Eliseo Belda, Marta Soler, Amalia Agut
"Ultrasound-guided 'two-in-one' femoral and obturator nerve block in the
dog: an anatomical study."

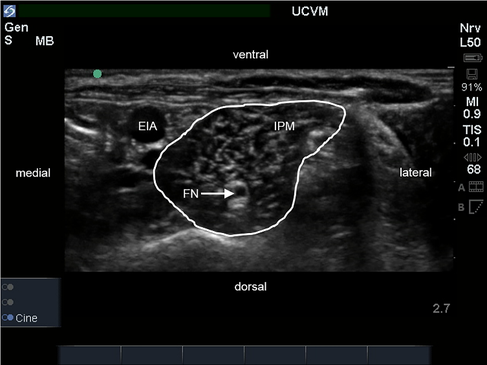
Ultrasound image of the iliopsoas muscle (IPM) in transverse section.
The external iliac artery (EIA) is located medial to the IPM and the femoral nerve (FN) is identified as a round hypoechoic structure within the muscle.
O. Cathasaigh M, Read MR, Atilla A, Schiller T, Kwong GPS (2018) "Blood concentration of bupivacaine and duration of sensory and motor block following ultrasound-guided femoral and sciatic nerve blocks in dogs." PLoS ONE 13(3): e0193400. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0193400

Ultrasound image of the lateral aspect of the pelvic limb.
The sciatic nerve (ScN) is located medial to the biceps femoris muscle and is identified as two ovoid hypoechoic structures with the cranial component (peroneal nerve) being smaller than the caudal component (tibial nerve) in transverse section.
O. Cathasaigh M, Read MR, Atilla A, Schiller T, Kwong GPS (2018) "Blood concentration of bupivacaine and duration of sensory and motor block following ultrasound-guided femoral and sciatic nerve blocks in dogs." PLoS ONE 13(3): e0193400. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0193400

Diese Webseite wurde mit Jimdo erstellt! Jetzt kostenlos registrieren auf https://de.jimdo.com