Article added / Artikel hinzugefügt 01.10.2021
Generally Articles and Discussions about Osteosarcoma in Dogs
→ Evaluations of phylogenetic proximity in a group of 67 dogs with
osteosarcoma: a pilot study
Article added / Artikel hinzugefügt 01.10.2021
Generally Articles and Discussions about Osteosarcoma in Dogs
→ Canine Periosteal Osteosarcoma
Images added / Abbildungen hinzugefügt 02.05.2019
Generally Sonography Atlas of Dogs →
Cardiovascular system → Pulmonary vessels
New subcategory added / Neue Unterkategorie hinzugefügt 02.05.2019
Generally Sonography Atlas of Dogs →
Cardiovascular system → Pulmonary vessels
Images added / Abbildungen hinzugefügt 01.05.2019
Generally Sonography Atlas of Dogs →
Cardiovascular system → Heart valvular diseases



Generally Sonography Atlas of Dogs
(Allgemeiner Sonographie-Atlas von Hunden)
Lymphatic system
(Lymphsystem)
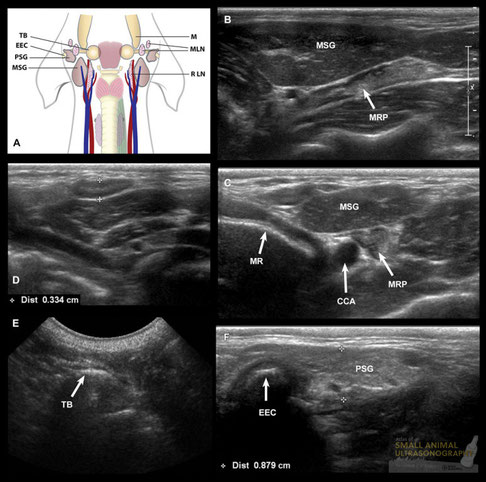
Normal lymph nodes and salivary glands.
A: Illustration of the anatomical location of these structures in the canine neck. TB, tympanic bulla; EEC, external ear canal; PSG, parotid salivary gland; MSG, mandibular salivary gland; M, mandible; MLN, mandibular lymph nodes; RLN, retropharyngeal lymph node. B and C: Sagittal (B) and transverse (C) sonographic images of the mandibular salivary gland (MSG) and medial retropharyngeal lymph nodes (MRP). Cranial is to the left of the image. The MSG has a striated echotexture with a central linear echo. It is adjacent to the more hypoechoic digastric muscle overlying the hyperechoic interface of the mandibular ramus (MR). The MRP lymph node is more echogenic and located obliquely dorsomedial to the salivary gland. The lymph node is located lateral to the common carotid artery (ECA) in the transverse plane (C). D. Sagittal sonographic image of one of the mandibular lymph nodes. This node shows a hypoechoic halo in this asymptomatic dog, and is considered normal. E. Sagittal sonogram of the tympanic bulla. Note the hyper convex interface with deep acoustic reverberation. F. Sagittal image of the normal parotid salivary gland (PSG), which is located caudal to the external ear canal (EEC). Note that le gland partly encircles the canal ventrally.
With special thanks to the authors of the book "Small Animal Ultrasonography" , Marc-André d’Anjou and Dominique Penninck

Fine needle aspiration in a mesenteric lymph node. The 22G needle is clearly visualizad from the right side entering the jejunal lymph node
Pablo Gomez Ochoa, Delia Lacasta, Ivan Sosa, Manuel Gascon, Juan Jose Ramos and Luis Miguel Ferrer (2011). Foundamentals and Applications of Abdominal Doppler, Ultrasound Imaging - Medical Applications, Prof. Oleg Minin (Ed.), ISBN: 978-953-307-279-1, InTech, DOI: 10.5772/20333. Available from: http://www.intechopen.com/books/ultrasound-imaging-medical-applications/foundamentals-and-applications-of-abdominal-doppler

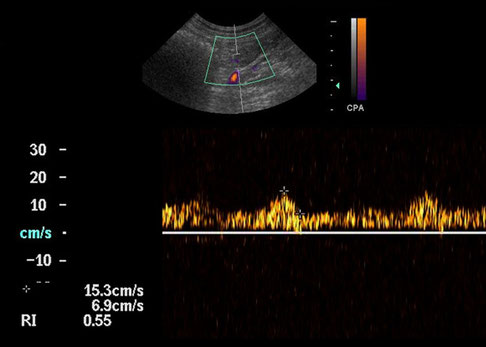
Spectral trace from a reactive mesenteric lymph node, showing a RI of 0.55
Pablo Gomez Ochoa, Delia Lacasta, Ivan Sosa, Manuel Gascon, Juan Jose Ramos and Luis Miguel Ferrer (2011). Foundamentals and Applications of Abdominal Doppler, Ultrasound Imaging - Medical Applications, Prof. Oleg Minin (Ed.), ISBN: 978-953-307-279-1, InTech, DOI: 10.5772/20333. Available from: http://www.intechopen.com/books/ultrasound-imaging-medical-applications/foundamentals-and-applications-of-abdominal-doppler

Spectral trace from a metastasic mesenteric lymph node from a ovaric carcinoma, showing a RI of 0.79
Pablo Gomez Ochoa, Delia Lacasta, Ivan Sosa, Manuel Gascon, Juan Jose Ramos and Luis Miguel Ferrer (2011). Foundamentals and Applications of Abdominal Doppler, Ultrasound Imaging - Medical Applications, Prof. Oleg Minin (Ed.), ISBN: 978-953-307-279-1, InTech, DOI: 10.5772/20333. Available from: http://www.intechopen.com/books/ultrasound-imaging-medical-applications/foundamentals-and-applications-of-abdominal-doppler

Cysterna chyli in a 10 year old Labrador dog with gastroenteritis. There was no peritoneal effusion or other signs of lymphatic congestion. The cysterna (arrowheads) appears as a well-defined cystic structure partly encircling the mid abdominal aorta on its dorsal left border. It appears fusiform in longitudinal plane (A) and oval to semicircular in transverse plane (B).
With special thanks to the authors of the book "Small Animal Ultrasonography" , Marc-André d’Anjou and Dominique Penninck

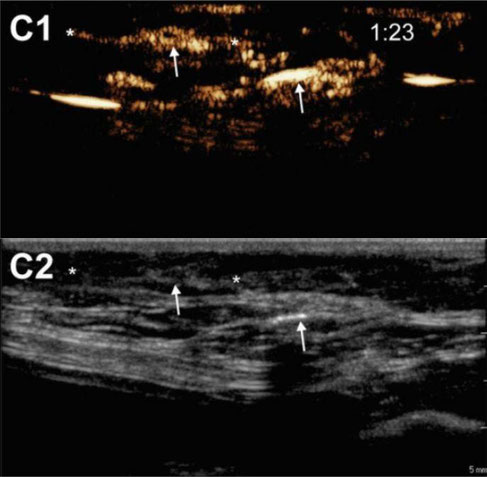
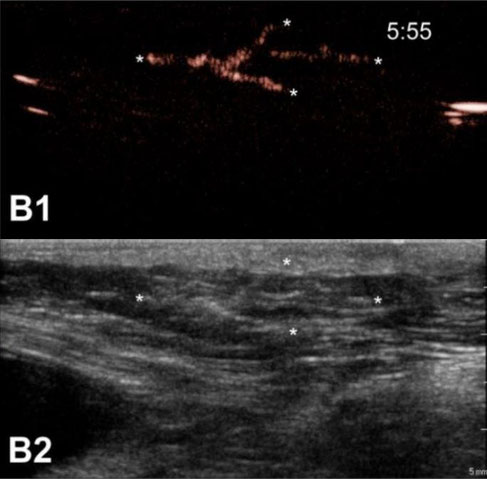
Influence of animal properties on the lymphatic CEUS images. Pictures show the CEUS images obtained after s.c. injection of unloaded microbubbles around the mammary glands of a male dog (A1), a spayed female dog (B1) and an intact female dog (C1). Respective B-mode images are shown in A2, B2 and C2. The injection site is indicated as “i.s.” (the injection site for images C1 and C2 is out of the field-of-view), arrows indicate the accumulation of microbubbles in the lymph nodes and lymph vessels are pointed out with asterisks. Time after microbubble injection is noted on the CEUS images (in min:s).
Heleen Dewitte, Katrien Vanderperren, Hendrik Haers, Emmelie Stock, Luc Duchateau, Myriam Hesta, Jimmy H. Saunders, Stefaan C. De Smedt, and Ine Lentacker
"Theranostic mRNA-loaded Microbubbles in the Lymphatics of Dogs: Implications for Drug Delivery" doi: 10.7150/thno.10298

Contrast agent migration from the injection site into the lymph vessels and nodes. Upon microbubble injection, unidirectional transport of microbubbles away from the injection site, through an afferent lymph vessel into a draining lymph node can be observed with CEUS (A1). Image (B1) shows the trafficking of microbubble contrast signal through branched lymph vessels. In (C1), the CEUS image shows a lymph node connected to one afferent lymph vessel and 3 efferent lymph vessels that take the contrast agents further away from the injection site. Corresponding B-mode images are shown in (A2), (B2) and (C2), respectively. Images were obtained after injection of mRNA-loaded microbubbles in different female dogs. The injection site is marked as “i.s.” (unless outside of the field-of-view), arrows indicate lymph nodes and asterisks point out lymph vessels. Time after microbubble injection is noted on the CEUS images (in min:s).
Heleen Dewitte, Katrien Vanderperren, Hendrik Haers, Emmelie Stock, Luc Duchateau, Myriam Hesta, Jimmy H. Saunders, Stefaan C. De Smedt, and Ine Lentacker
"Theranostic mRNA-loaded Microbubbles in the Lymphatics of Dogs: Implications for Drug Delivery" doi: 10.7150/thno.10298

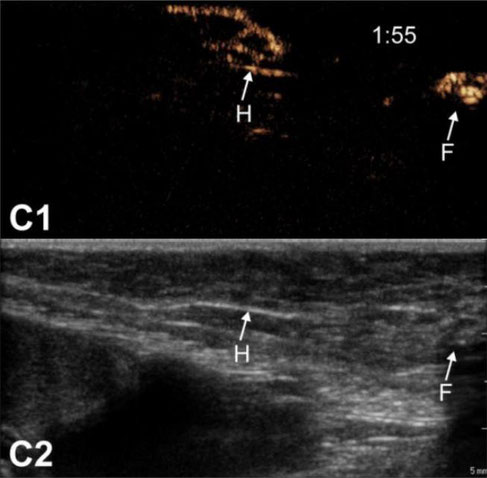
Lymph node anatomy observed by CEUS. CEUS can be used to identify the relation between afferent lymph vessels and draining lymph nodes. Lymph vessels either distribute their content within the lymph node (“filled” nodes, A1-A2) or they go around the lymph nodes without discharging its contents into the node (“hollow” nodes, B1-B2 and C1-C2). In the latter scenario, we always observed a node with a “hollow” appearance (indicated as “H”), followed by a more distant “filled” node (indicated as “F”). Images were obtained from 3 different animals. Where possible, the injection site is pointed out as “i.s.”. Time after microbubble injection is noted on the CEUS images (in min:s).
Heleen Dewitte, Katrien Vanderperren, Hendrik Haers, Emmelie Stock, Luc Duchateau, Myriam Hesta, Jimmy H. Saunders, Stefaan C. De Smedt, and Ine Lentacker
"Theranostic mRNA-loaded Microbubbles in the Lymphatics of Dogs: Implications for Drug Delivery" doi: 10.7150/thno.10298

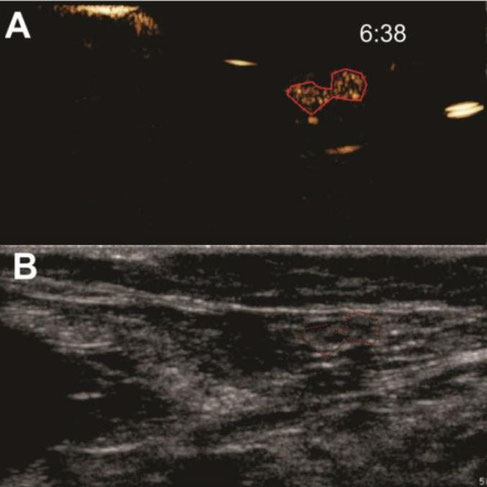
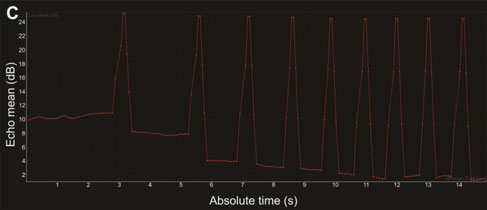
Burst destruction of intranodal microbubbles. After visualization of unloaded microbubble drainage, the scanner's burst function was used to destroy the microbubbles within the lymphatics. Images show (A) CEUS image with a ROI drawn around a lymph node filled with mRNA-loaded microbubbles and (B) the corresponding B-mode image. Burst analysis is represented in (C) as the echo mean (dB), where each burst is visible as an echo mean peak, followed by a reduction of the contrast echo mean. Time after mRNA-loaded microbubble injection is noted on the CEUS images (in min:s).
Heleen Dewitte, Katrien Vanderperren, Hendrik Haers, Emmelie Stock, Luc Duchateau, Myriam Hesta, Jimmy H. Saunders, Stefaan C. De Smedt, and Ine Lentacker
"Theranostic mRNA-loaded Microbubbles in the Lymphatics of Dogs: Implications for Drug Delivery" doi: 10.7150/thno.10298

CEUS imaging of a vast lymphatic network in an intact female dog. After s.c. injection of unloaded microbubbles around the mammary glands of an intact female dog, a vast lymphatic network could be observed with CEUS imaging.
Heleen Dewitte, Katrien Vanderperren, Hendrik Haers, Emmelie Stock, Luc Duchateau, Myriam Hesta, Jimmy H. Saunders, Stefaan C. De Smedt, and Ine Lentacker
"Theranostic mRNA-loaded Microbubbles in the Lymphatics of Dogs: Implications for Drug Delivery" doi: 10.7150/thno.10298

CEUS imaging of 2 lymph vessels connected to one lymph node. Images were recorded after s.c. injection of mRNA-loaded microbubbles in an intact female dog.
Heleen Dewitte, Katrien Vanderperren, Hendrik Haers, Emmelie Stock, Luc Duchateau, Myriam Hesta, Jimmy H. Saunders, Stefaan C. De Smedt, and Ine Lentacker
"Theranostic mRNA-loaded Microbubbles in the Lymphatics of Dogs: Implications for Drug Delivery" doi: 10.7150/thno.10298

CEUS of mRNA-loaded microbubbles 6 min after mRNA-loaded microbubble injection. Images were recorded 6 min after injection of mRNA-loaded microbubbles in a spayed female dog.
Heleen Dewitte, Katrien Vanderperren, Hendrik Haers, Emmelie Stock, Luc Duchateau, Myriam Hesta, Jimmy H. Saunders, Stefaan C. De Smedt, and Ine Lentacker
"Theranostic mRNA-loaded Microbubbles in the Lymphatics of Dogs: Implications for Drug Delivery" doi: 10.7150/thno.10298

Burst destruction of intranodal microbubbles. After injection of
unloaded microbubbles in an intact female dog, multiple bursts were delivered to destroy the intranodal microbubbles and reduce the mean echo intensity.
Heleen Dewitte, Katrien Vanderperren, Hendrik Haers, Emmelie Stock, Luc Duchateau, Myriam Hesta, Jimmy H. Saunders, Stefaan C. De Smedt, and Ine Lentacker
"Theranostic mRNA-loaded Microbubbles in the Lymphatics of Dogs: Implications for Drug Delivery" doi: 10.7150/thno.10298

Planes of the lymph nodes used to obtain measurements: (A) sagittal plane for maximum length (a) and thickness (b); (B) dorsal plane for maximum width (c) in the short axis.
Pugliese M, La Pietra A, Liotta L, Macri F, Palumbo Piccionello A, De Majo M (2016): "Ultrasonographic measurements of abdominal lymph nodes in growing puppies". Veterinarni Medicina, 61: 389-393

Reactive lymph nodes in dogs
Changes in size, shape, contour, echogenicity and echotexture are signs of some inflammatory process (lymphadenopathy), which has to be differentiated from benign malignant alteration.
Internal lymph node changes tend to be more affected by neoplasms. Inflammatory lymph nodes are generally poorly defined and hyperechoic thread; The non-inflamed malignants have a more pronounced
contour and there may be acoustic and hypoechoic reinforcement.
Below are two distinct cases of dogs with regional lymph nodes enlargement, with changes in hepatic (coarse) and splenic (renatured) parenchyma:
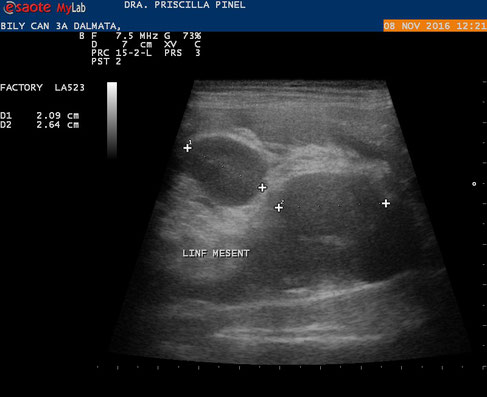
Canine of the Dalmatian breed of 3 years, with enlargement of regional lymph nodes (splenic, mesenteric, hepatic, renal, intestinal) ... and subcutaneous (submandibular, popliteal, axillary, inguinal):
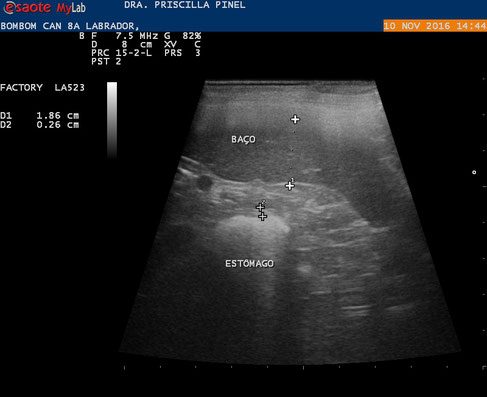
8-year-old Labrador canine with increased lymph nodes similar to the animal at the top:
With special thanks to Priscilla Pinel, Medical Veterinary.
Currently serves in veterinary clinics and homes for the municipality of Rio de Janeiro ( south, north and west ).
http://veterinariapriscillapinel.com.br

B-Mode ultrasound images of a canine loco regional lymph nodes.
(A) inguinal lymph node with metastasis note the elongated shape. (B) normal inguinal lymph node. (C) axillary lymph node with metastasis note the rounded shape. (D) normal axillary lymph node.
Priscila Silva, Ricardo Andres Ramirez Uscategui, Marjury Cristina Maronezi,
Beatriz Gasser, Letícia Pavan, Igor Renan Honorato Gatto, Vivian Tavares de Almeida,
Wilter Ricardo Russiano Vicente & Marcus Antônio Rossi Feliciano: "Ultrasonography for lymph nodes metastasis identification in bitches with mammary neoplasms"; Scientific Reports volume 8, Article number: 17708 (2018)

Colour Doppler ultrasound images of canine loco regional lymph nodes.
(A) Normal axillary lymph node with absence of vascularization. (B) Axillary lymph node with metastasis and presence of neovascularization, (C) normal inguinal lymph node with absence of vascularization and (D) inguinal lymph node with metastasis and presence of neovascularization.
Priscila Silva, Ricardo Andres Ramirez Uscategui, Marjury Cristina Maronezi,
Beatriz Gasser, Letícia Pavan, Igor Renan Honorato Gatto, Vivian Tavares de Almeida,
Wilter Ricardo Russiano Vicente & Marcus Antônio Rossi Feliciano: "Ultrasonography for lymph nodes metastasis identification in bitches with mammary neoplasms"; Scientific Reports volume 8, Article number: 17708 (2018)

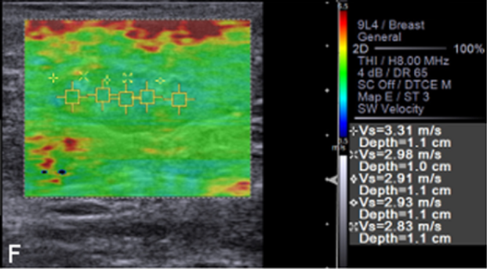
Qualitative and quantitative ARFI-elastography images of (A) normal axillary lymph node, (B) normal inguinal lymph node with homogeneous pattern and SWV in m/s. (C) Reactive axillary lymph node, (D) reactive inguinal lymph node with heterogeneous pattern and SWV in m/s. (E) Axillary lymph node with metastasis, (F) inguinal lymph node with metastasis with heterogeneous pattern and SWV in m/s.
Priscila Silva, Ricardo Andres Ramirez Uscategui, Marjury Cristina Maronezi,
Beatriz Gasser, Letícia Pavan, Igor Renan Honorato Gatto, Vivian Tavares de Almeida,
Wilter Ricardo Russiano Vicente & Marcus Antônio Rossi Feliciano: "Ultrasonography for lymph nodes metastasis identification in bitches with mammary neoplasms"; Scientific Reports volume 8, Article number: 17708 (2018)

Diese Webseite wurde mit Jimdo erstellt! Jetzt kostenlos registrieren auf https://de.jimdo.com